Wrist Fracture
A wrist fracture is a break in one or more of the bones in the wrist. The wrist is made up of the two bones in the forearm called the radius and the ulna. It also includes eight carpal bones. The carpal bones lie between the end of the forearm bones and the bases of the fingers. The most commonly fractured carpal bone is called the scaphoid or navicular bone.
This fact sheet will focus on fractures of the carpal bones of the wrist.
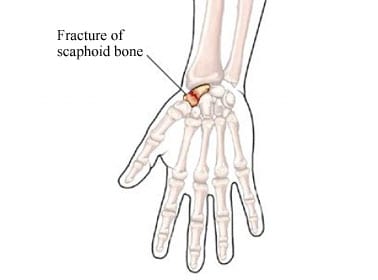

Copyright © Nucleus Medical Media, Inc.
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
A wrist fracture is caused by trauma to the bones in the wrist. Trauma may be caused by:
- Falling on an outstretched arm
- Direct blow to the wrist
- Severe twist of the wrist
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
Factors that increase your chance of developing a wrist fracture include:
- Participating in contact sports, such as football or soccer
- Participating in activities such as in-line skating, skateboarding, or bike riding
- Participating in any activity which could cause you to fall on your outstretched hand
- Violence or high-velocity trauma, such as an automobile accident
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
Factors that increase your chance of developing a wrist fracture include:
- Participating in contact sports, such as football or soccer
- Participating in activities such as in-line skating, skateboarding, or bike riding
- Participating in any activity which could cause you to fall on your outstretched hand
- Violence or high-velocity trauma, such as an automobile accident
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, physical activity, and how the injury occurred. The injured area will be examined. Images may need to be taken of your wrist. This can be done with:
- X-rays
- MRI scan —rarely
- CT scan —rarely
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library Resources
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- The American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine
CANADIAN RESOURCES:
- Canadian Orthopaedic Association
- Canadian Orthopaedic Foundation
REFERENCES:
- Distal radius fracture. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons website. Available at: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00412 . Updated August 2007. Accessed March 12, 2013.
- Distal radius fracture. EBSCO DynaMed website. Available at: https://dynamed.ebscohost.com . Updated December 17, 2012. Accessed March 12, 2013.
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library