Shin Splints
Medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS) is exercise-related pain in the shins. It may be caused by an irritation of the tendons and muscles near the shin bones. MTSS is commonly known as shin splints. This injury is most often seen among runners.
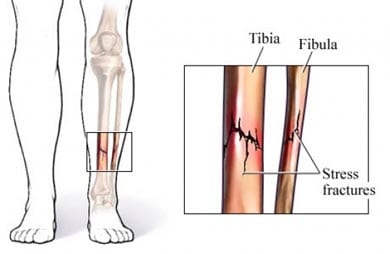

Copyright © Nucleus Medical Media, Inc.
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
The exact cause is unknown. MTSS is called an overuse injury. It most commonly occurs from repetitive motion or stress at the shins. Causes may include:
- Acute inflammation of structures in the calf
- Chronic compartment syndrome
- Chronic trauma to structures in the calf
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
These factors increase your chance of MTSS. Tell your doctor if you have any of these risk factors:
- Participation in repetitive, high-impact sports
- Running
- Gymnastics
- Basketball
- Racquet sports
- Military recruits
- Female runners with amenorrhea (absent menstruation) and osteoporosis
- Pronation of feet (feet turn inwards), or other leg or foot abnormalities
- Poor (hard) running surfaces
- Poor footwear
- Overtraining or recent increase in workout or miles run
- Heel cord tightness
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
If you have any of these symptoms do not assume it is due to MTSS. These symptoms may be caused by other conditions. Tell your doctor if you have any of these:
- Shin pain at a very specific point
- Pain when running which gets more severe with continued exercise
- Pain when bearing weight on the leg
- Pain after changing workout intensity or running surface
- Symptoms may not go away with rest
- Swelling
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
Your physician may prescribe physical therapy. Depending upon the severity of your injury, your physical therapy treatment may include:
- Pain reduction: The RICE principle is the first step to recovery (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Manual therapy and Kinesiotaping may also be used to speed up recovery and reduce swelling.
- Increase Range of Motion (ROM) & strengthening: Your physical therapist will prescribe stretches and exercises that are designed to correct movement patterns, promote proper healing of the muscles, and reduce the risk of future injuries. A home exercise program may also be implemented.
- Custom orthotics/gait analysis: Your physical therapist may evaluate your foot and & running technique to determine the cause of the injury. Your therapist may also recommend a custom foot orthotic to wear in your shoes in order to prevent re-injury. If you are a runner, a gait analysis may also be done. A gait analysis quantifies your running mechanics to help determine and modify movements to reduce the risk of further damage.
- Return to sport: If you are an athlete, your therapist may tailor exercises that are specific to strengthening the areas needed to perform your sport. Modified use of your muscles may also be discussed and implemented. Return to your sport may be gradual to prevent re-injury.
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
To help reduce your chance of getting MTSS, you may try the following steps:
- Wear shock-absorbing insoles when running or during other high-impact exercise.
- Stretch before and after exercising.
- When starting a new sport or increasing your workout, do so gradually.
- Choose footwear that is best for the activity and your foot.
- Cross train.
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library
This content was created using EBSCO’s Health Library